

< Previous | Contents | Next >
Section 5 Longitudinals
501. Spacing
The standard spacing of longitudinals is obtained from the following formula:
Ċ Ņ Ī Ã Ñ JJL (mm)
502. Scantlings
1. The section modulus of bottom longitudinals is not to be less than obtained from the following for- mula, but in no case is it to be less than 30 cm3.
Ěᾎ Ņ
ǼĊᾜᾨ Ī (cm3)
where:
ᾨ = Spacing of solid floors (m)
Ċ = Spacing of longitudinals (m)
ᾜ = Vertical distance from the longitudinals to a point of ᾘ Ñ LǾLĪĴ Ã above the top of keel (m)
Ǽ = Coefficient given in Table 8.1.
Table 8.1 Coefficient Ǽ
Case | Ǽ | |
In case where no strut specified in 503. is provided midway between floors | 8.6 | |
In case where a strut specified in 503. is provided midway between floors. | Lower part of deep tanks | 6.2 |
Elsewhere | 4.1 | |
2. The section modules of inner bottom longitudinals is not to be less than obtained from the formula Par 1 with Ǽ equal to 0.85 times the value specified for bottom longitudinals in the same location. Where vertical struts are not provided to the longitudinals under deep tanks, the section modules of inner bottom longitudinals is to be as specified in Ch 15, 202.
503. Vertical struts
1. Where the spacing of solid floors exceeds 2.5 m, This strut is to be a rolled section other than a
a strut is to be provided between floor plates. f1at bar or a bulb plate and to be sufficiently
![]()
overlapped with the webs of bottom and inner bottom longitudinals.
2. The sectional area of vertical struts is not to be less than obtained from the following formula:
A Ņ ĪǾĪ Ċᾎᾜ (cm2) where:
Ċ = Spacing of longitudinals (m)
ᾎ = Breadth of the area supported by the strut (m). (See Fig 8.1)
ᾜ = As specified in 502. 1.
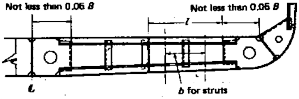
Fig 8.1. Open floor